The hierarchy of biological needs and other human needs – drawn up by Russian psychologist Abraham Maslow – could be more useful to your life than you currently realize…
At first glance, this project may seem like a list of things that a person needs…
However, when you take the time to really understand this project, it can answer deeper questions about human psychology, motivation and personal growth that have perplexed us for centuries…
Have you ever stopped to ponder what you’re really after during your time here on this planet? Do you question why you don’t have the motivation to chase grander and more meaningful projects?
These are types of questions that I help people answer in my role as a life coach – and Maslow’s Hierarchy Of Needs proves very useful in this context.
That’s why I’m excited to share this deep dive into Maslow’s Hierarchy Of Needs – and how it can help you understand what you really want to do with your life.
So, let’s dive in.

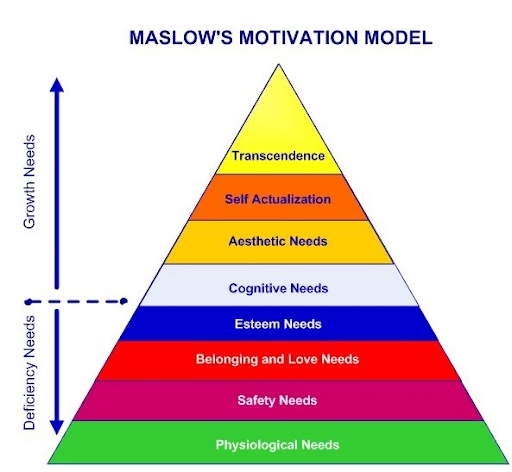
What Is Maslow Hierarchy Of Needs?
Psychologist Abraham Maslow created his hierarchy of needs to answer the often-answered question about what is most important in life to humans.
It has achieved great significance in the studies of human psychology. It’s one of the most cited studies in examples of what motivates human behavior.
His original hierarchy was a five-stage model. It has since been updated to include seven and then eight basic needs.
These needs were ordered, according to their importance to humans. Maslow initially argued that people must satisfy all lower level needs before progressing onto higher-level needs. However, he later suggested that his hierarchy wasn’t as rigid as that.
All human behavior can be explained by the needs in this list. Still, it can be agreed that people will find it difficult to try and fulfil higher-level needs if we have unmet needs below them in the hierarchy.
Maslow explained: “It is quite true that man lives by bread alone — when there is no bread. But what happens to man’s desires when there is plenty of bread and when his belly is chronically filled?
“At once, other (and “higher”) needs emerge and these, rather than physiological hungers, dominate the organism. And when these in turn are satisfied, again new (and still “higher”) needs emerge and so on. This is what we mean by saying that the basic human needs are organized into a hierarchy of relative prepotency”
What Are The 7 Basic Human Needs?
Below, we’ll explore the first 7 categories of human needs according to Abraham Maslow – and list some examples of the basic needs in each category.
We’ll also touch on the eighth and highest human need added in the 1970s.
These categories are listed in order of importance to human beings.
Basic Physiological Needs
- Air
- Food
- Drink
- Shelter
- Warmth
- Sleep
Maslow considered physiological needs the most important to humans. Indeed, air is the most urgent need for our survival. The ability to stay hydrated and fed comes shortly afterwards in terms of urgency.
Without these absolute basic necessities, you won’t last more than a couple of days on this planet (or minutes in the case of air). As such, all the other needs will pale in importance.
The other most basic physiological needs include shelter, warmth and sleep. Without these physiological needs, human survival is again at risk. Even if you have enough to survive but not enough for the human body to be comfortable, it will be difficult to focus on any higher goals.
Safety Needs
- Security
- Law
- Order
- Stability
- Freedom from fear of death
Physiological and safety needs both focus on human survival. If your safety needs aren’t fulfilled, you might not be at such an immediate risk of death, compared to your most basic physiological needs.
However, your well-being will be threatened enough that it’s near-on impossible to focus on any other higher-level goals.
Love and Belongingness Needs
- Acceptance
- Friendship
- Intimacy
- Sense Of Belonging
According to Maslow, our social needs rank just above staying alive. That’s how important people find it to ‘fit in’ to society. It’s a basic need hard-wired into our psychology.
Some authors list love in this category, although the feeling of love is arguably a combination of the four basic needs listed above.
It’s also some authors list sex among the basic physiological needs, while others include it here alongside among intimacy.
Although sex is undeniably an important biological need to humans, it’s hard to argue the case of it being as important to our survival as food, water or any safety needs.
For more on this topic: check out my guide on Needs vs Wants In Relationships.
Esteem Needs
- Dignity
- Achievement
- Mastery
- Independence
- Status
- Prestige
Maslow defined esteem needs as having two separate categories of equal importance. These are self-esteem (dignity, achievement, mastery, independence) and the need to be valued by others (status, prestige).
Many life coaches will tell you that self-esteem is more important, and that you need to learn to love yourself first. At the same time, it’s difficult to deny the biological human motivation to be accepted by our community.
Cognitive Needs
- Knowledge and understanding
- Exploration
- The need for meaning
Cognitive needs were added to Maslow’s Hierarchy Of Needs a couple of decades after the five-stage model was first published.
Indeed, it’s difficult to deny that many humans will seek a greater understanding of what they are doing here in this world, although only once their basic emotional and physical needs are met.
Perhaps it’s your cognitive needs that led you to this article in the first place.
Still, there’s no way they can be deemed as important to people as certain basic needs like food, water, safety or even our social status. A tired and hungry student will have little interest in studying, while their focus is tied to basic lower-level needs like food and sleep. Yes, they can try to overpower the basic needs of the human body for a short time, but they will ultimately fail.
Aesthetic Needs
- Appreciation and search for beauty
- Balance and form
- Image
This is another category added decades after the initial five-stage model of Maslow’s Hierarchy Of Needs.
The importance of ‘good looks’ is often debated in psychological discussions, but Maslow determined it to have enough significance to human motivation to add it into his hierarchy, albeit reasonably high up.
It’s hard to deny that a lot of human behavior is motivated by this desire, whether that’s buying designer clothes or plowing our faces with make-up every day. However, it could be argued that this stems from the strong desire for love from others, rather than beauty for beauty’s sake.
Self-Actualization Needs
- Fulfilling your full potential
- Self-fulfillment/self-understanding
- Enjoying ‘peak experiences’
- Creating a legacy
- Making the world a better place
- Presence
- Appreciation for life
Self-actualization was at the top of Maslow’s initial five-stage model.
The definition of self-actualization is somewhat flexible. Maslow’s later work focused on defining a self-actualized person, although his conclusion was somewhat broad. He listed 15 examples of characteristics that a self-actualized person could have in theory, and suggested that non-self-actualized people may show some of them too.
According to Maslow, the ability to fulfil your full potential would be the most important characteristic of a self-actualized person.
He estimated that only two per cent of people will ever reach self-actualization.
The 8th Human Need: Self-Transcendence Needs
- Mystical Experiences
- Outer-Body Experiences
- Religious Faith Or Discovery
This new level of personal growth was added as the highest of the human needs in the 1970s. It includes any experience which allows people to transcend beyond the personal self.
Its significance to the human experience can be questioned, but similarly to aesthetic needs, there are arguably enough people motivated by this form of growth to warrant its inclusion.
Related content: Tony Robbins 6 Human Needs Test
Frequently Asked Questions About Biological Needs
Here are some quick answers to frequently asked questions about a human’s most basic needs.
What Are The Six Basic Biological Needs?
The six most basic biological requirements listed at the bottom of Maslow’s hierarchy are: air, food, drink, shelter, warmth and sleep. These physical requirements are deemed as the most urgent needs among humans.
Are Biological Needs Primary Needs?
Yes, according to Abraham Maslow anyway. He put biological needs at the bottom of his hierarchy of needs, meaning they are of primary importance to the well-being of humans.
Psychological Needs Examples
Maslow’s Hierarchy Of Needs is sometimes divided into material and psychological needs. Indeed, almost everything above the lowest-level physical needs could be defined as psychological needs.
Psychological needs are everything in the following categories:
- Love and Belongingness Needs
- Esteem Needs
- Cognitive Needs
- Self-Actualization Needs
- Transcendence Needs
Social Needs
Social needs aren’t included as an official category. Rather, they are scattered across two categories: Love and Belongingness & Esteem.
Make no mistake about it, Maslow agreed that humans are inherently social creatures.
His hierachy of needs stated that social needs are very important to us, albeit not as important as our basic physiological needs or safety needs.
Essentially, he’s suggesting that being popular isn’t so important when you’re worried about staying alive.
How To Become Self-Actualized
Maslow created a list of 15 examples of characteristics of self-actualized people, based on a study of 18 famous people he considered to have reached this level of personal growth.
These characteristics were:
- A strong tolerance of uncertainty;
- Acceptance of themselves and others for who they are;
- Spontaneity
- Problem-centered (not self-centered);
- A unique sense of humor;
- The ability to look at life objectively;
- Creativity;
- Resistance to enculturation;
- Concern for human welfare;
- A deep appreciation for life;
- Has deep relationships with a few people;
- A desire for ‘peak experiences’
- Desire for privacy;
- A democratic attitude;
- Strong morale.
Maslow said that these characteristics can be developed by non-self-actualized people.
However, it’s safe to assume that most people would only develop an interest in developing them after their basic needs were met.
The satisfaction of biological systems, physiological and psychological needs always comes before personal growth.
Any More Questions About Our Basic Needs?
Thanks for reading my guide about the basic needs of a human being.
If you have any questions about Maslow’s Hierarchy Of Needs or the needs of the human race in general, leave a comment below.
Was a basic need missed? Do you disagree with the order of Maslow’s Hierarchy? Let me know!
I’d be excited to read and answer your query.
Related Posts
21 Facts – What Does Cheating Say About A Person?
21 CLEAR Signs Of Introvert Burnout & Effective Coping Strategies
